
Education & Resources
In dry landscapes such as those in the southwest desert, droughts and extreme heat are prominent components of the climate. In order to effectively conserve water and maintain the livelihood of the natural flora of the Sonoran desert, it is crucial to implement water conservation techniques that include both active and passive systems. Passive water systems are a low-maintenance and inexpensive way to provide water to personal landscaping while reducing home water usage. Passive systems can be used individually, or can be combined with active systems such as rainwater harvesting and gray water to increase water yields. These water conservation methods are especially vital to implement in drought prone areas and deserts, as water is especially scarce and the average family wastes approximately 9,400 gallons per year (US EPA).

On a grander scale regarding climate change, water conservation is one of the main components of keeping Earth livable, since the world’s water supply is not infinite and preservation of current resources is vital. Here at SERI, we are encouraging water preservation and resourcefulness by providing availability to these mitigation tactics to people of all economic statuses, specifically those financially struggling. Vulnerable communities are often given less access to financial support regarding sustainability issues even though they are disproportionately affected, so our goal is to provide these communities with sustainable water usage by reducing the financial burden of these implementations.
Rainwater Harvesting
One of the most efficient ways to conserve water and take advantage of weather patterns for personal benefit is to implement a rainwater harvesting system into your home. A cistern can be placed outside of your home to collect rainwater, which can then be used towards landscaping. In conjunction with passive systems such as berms and swales and watering basins, plants will be supplied with ample hydration solely from collected rainwater. When implementing a water conservation measure such as rainwater harvesting in a drought impacted area, developing a sustainable and water-efficient landscape with drought resistant flora is encouraged in order to maximize water usage.
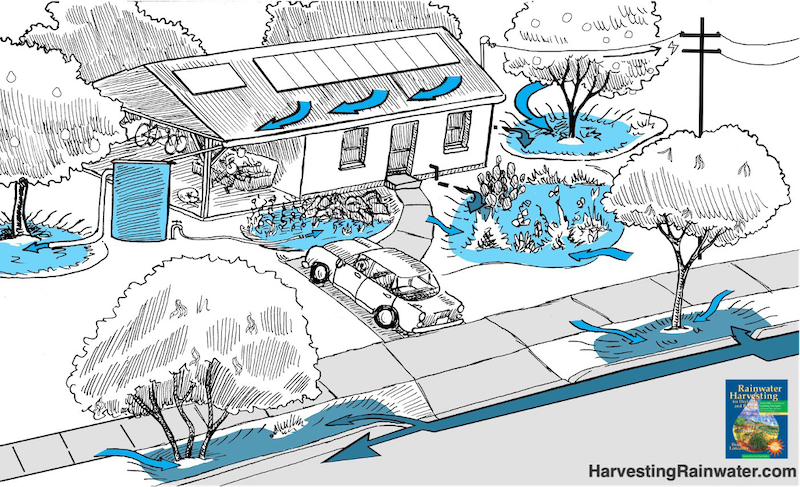

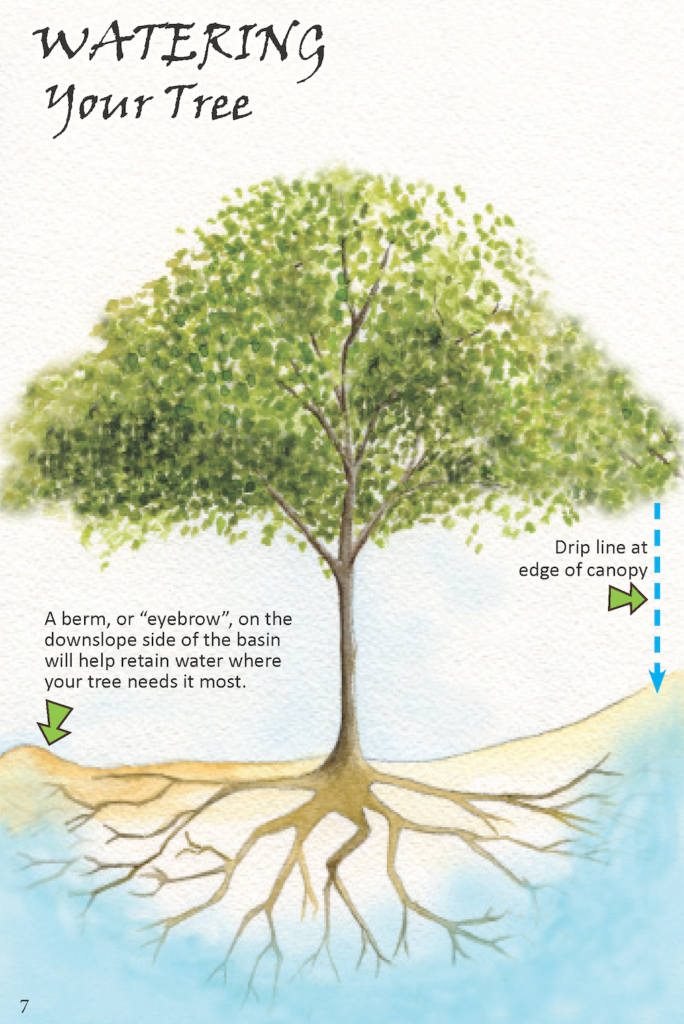
Water basins surrounding plants encourage slow and thorough soaking of the soil, which is a demonstration of a passive water system. When creating your own passive water system, first observe where water naturally flows when present in your yard. These water trails are a guideline for where streambeds and basins should be placed. To maintain passive water systems simply make sure that rocks and plants are staying in place and that water is flowing evenly without disruptions.
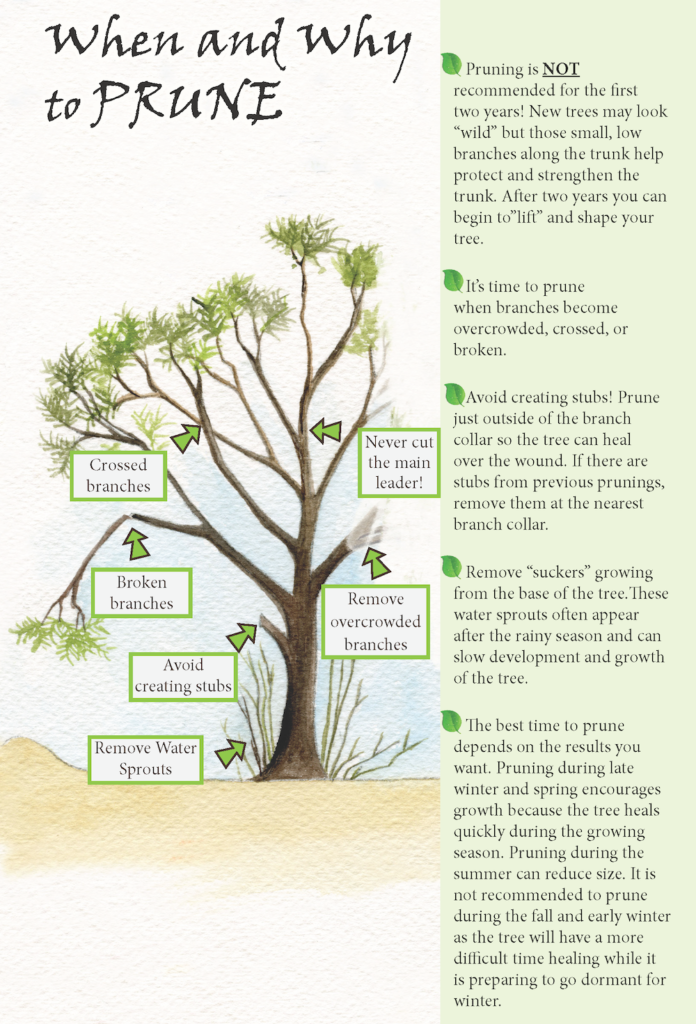
Landscape Management Practices to Optimize Passive Rainwater Harvesting and Plant Health
Drought Tolerant Plants and Trees
Suggested native and drought resistant flora that can be planted include lantana, yucca, agave, mesquite, saguaro, sage, and Mexican bird of paradise. Most varieties of cacti and succulents are also naturally drought tolerant and are suitable plants for desert landscaping. When maintaining plants in drought prone climates it is important to keep the soil healthy and moist, which can be supplemented with the addition of mulch to the top layer of soil. When watering, keep in mind that the frequency of watering changes by season and the amount of water given to the plants varies based on plant species.
Backyard Gardener – Tree Irrigation During Drought – August 26, 2020
Maintaining Landscapes During Heat and Drought | Cooperative Extension | The University of Arizona
The Essential Guide to Drought Tolerant Plants for Arizona
Gray Water Harvesting
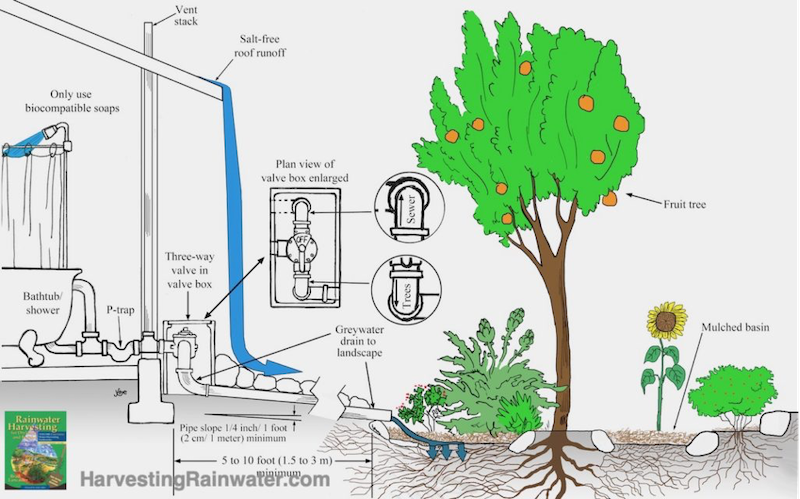
Gray water is repurposed water coming from your washing machines, showers, and sinks that has not been contaminated by fecal matter or other toxic components. Although it is not necessarily “clean” water, it is completely suitable to be used on ornamental plants or an assortment of trees, including fruit trees. This method of water conservation is recommended for those who desire a low maintenance way to reduce water wastage in their home and don’t mind using eco-friendly cleaning and laundry products. It is important with gray water usage to monitor what you’re putting into your washing machine, as sodium, bleach, borax, and other chemicals can be detrimental to your plants.
Frequently Asked Questions
If you are looking for an inexpensive, easy to set up system that takes advantage of rainfall without any work (besides maintenance) on your end, then a passive system would be a great option. If you are looking to reduce your water usage directed towards landscaping purposes and desire a higher yield of water, although it is more expensive, an active system would be best to meet your needs.
With a passive system, nothing is required on your end except for occasional maintenance and supplemental watering during dry seasons. For active systems, a rainwater cistern includes a spout on the side that can be connected to a hose or tube to water vegetation, and gray water systems have a tube that can be placed by the plants or trees that need to be watered.
Installation of passive water systems is a straightforward and simple process, depending on the complexity of your system. To create water basins, simply dig 6-12 inches into the soil around your in-ground plants or trees. Then, line the outer rim of the basin with medium sized rocks in order to keep water in the basin and add a layer of mulch on top of the soil to retain nutrients and moisture. Dry streambeds lined with rocks can be made around basins in order to encourage water flow from one basin to another, or to outer areas of a yard.
